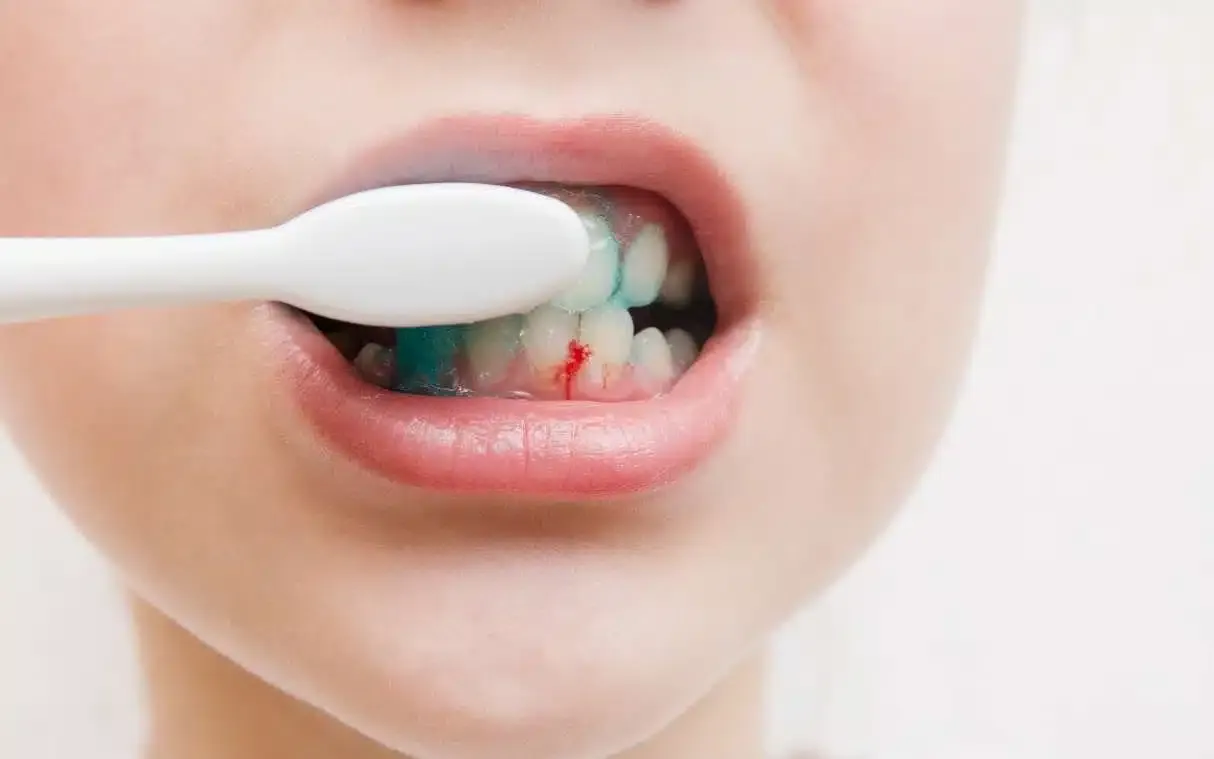
You’re brushing your teeth as usual when you notice a trace of pink in the sink. It’s easy to shrug off after all, a little bleeding now and then might seem harmless. But while bleeding gums are common, they’re not normal. Bleeding gums are your body’s way of saying something’s wrong. It could be simple irritation, poor brushing habits, or the early stages of gum disease. The good news is that, in most cases, bleeding gums are reversible with the right care.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes of bleeding gums, what to do if it happens, and how to prevent it from recurring. Understanding the reason behind the bleeding is the first step toward restoring your gum health and protecting your smile.
Occasional gum bleeding especially after flossing for the first time in a while can happen. However, healthy gums should not bleed regularly. If your gums bleed often, it’s a sign of irritation or inflammation known as gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Ignoring bleeding gums can allow gingivitis to progress into periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease that can damage bone and lead to tooth loss. So, while it might seem minor, persistent gum bleeding is a warning sign you shouldn’t ignore. Addressing it early means easier, faster treatment and healthier gums in the long run.
When plaque a sticky film of bacteria builds up on your teeth, it irritates the gumline and triggers inflammation. Over time, this leads to redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing.
You might think brushing harder cleans better but aggressive brushing actually damages your gums and enamel. This can cause tenderness, recession, and bleeding.
If you’ve just started flossing again after a long break, you might notice some bleeding that’s your gums adjusting to the new routine.
Vitamins C and K play important roles in gum health and wound healing. A deficiency can make your gums more prone to bleeding.
Hormone fluctuations can make gums more sensitive and reactive to plaque, leading to temporary bleeding or swelling a condition often called “pregnancy gingivitis.”
Certain medications like blood thinners, or conditions like diabetes and immune disorders, can increase gum bleeding.
Solution: Don’t stop prescribed medication but do inform your dentist. They can adjust your care plan to minimize gum irritation and bleeding.
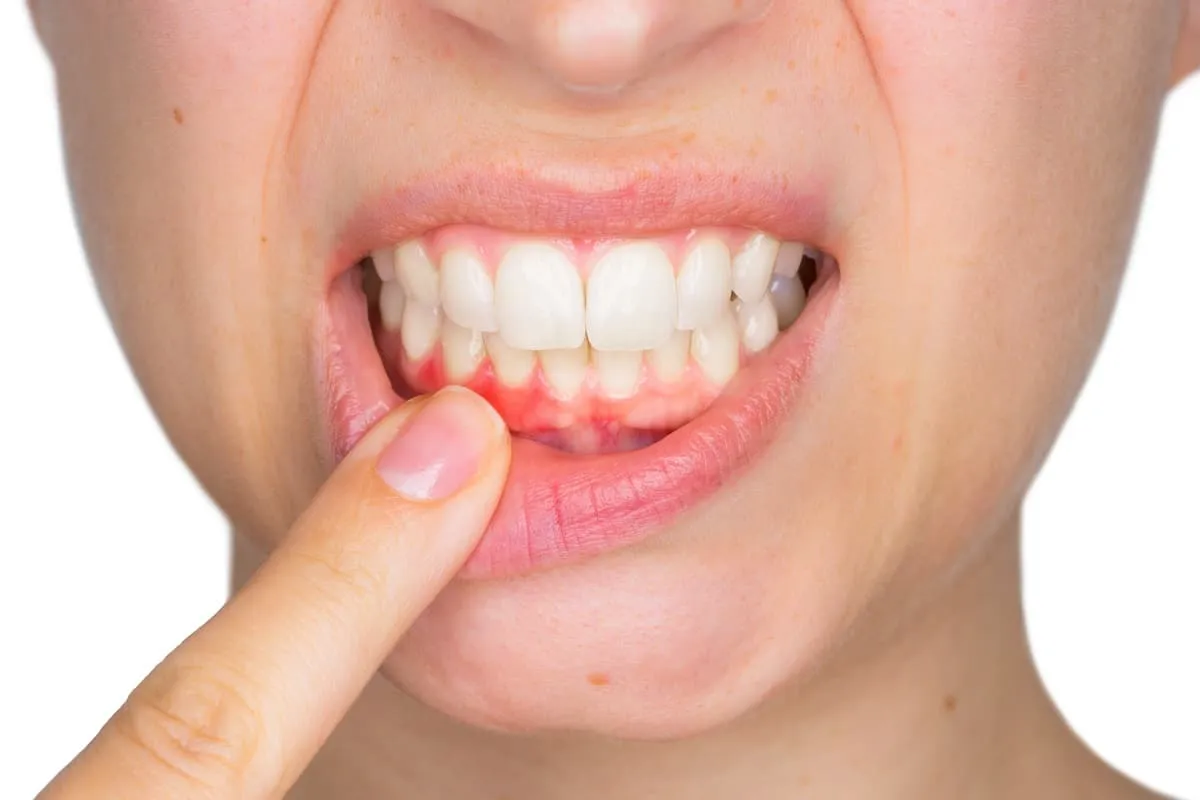

If you notice bleeding gums, don’t panic and don’t stop brushing. Here’s what you should do:
Brush gently using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
Floss daily using proper technique to clean between teeth without cutting the gums.
Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and K to strengthen gum tissue.
Stay hydrated saliva helps protect and clean the mouth naturally.
Avoid tobacco, as smoking weakens gums and delays healing.
Schedule a dental cleaning plaque and tartar removal is essential to stop gum irritation.
With consistent care, bleeding often subsides within a week or two. If it doesn’t, professional evaluation is necessary.
When to See a Dentist
See your dentist as soon as possible if you notice:
Bleeding that lasts more than a week.
Gums that are swollen, red, or tender.
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
Receding gums or loose teeth.
Pus, pain, or signs of infection.
These symptoms suggest advanced gum disease (periodontitis), which requires professional treatment to prevent tooth and bone loss. Early intervention makes a huge difference in preserving your oral health.
Professional Treatments for Bleeding Gums
If your gums continue to bleed despite good oral hygiene, it’s a sign that professional dental treatment may be necessary. Bleeding gums often indicate gum inflammation (gingivitis) or the early stages of gum disease, which cannot always be reversed through home care alone. Your dentist will carefully examine your mouth, measure the depth of your gum pockets, and determine the most effective treatment plan based on the severity of your condition.
Here are the most common professional treatments used to restore gum health and prevent further damage:
Professional Cleaning (Scaling and Polishing)
This is the first line of defense against bleeding gums. During a professional cleaning, your dentist or hygienist removes plaque, tartar, and bacteria that regular brushing can’t reach especially around and below the gumline. Polishing smooths the tooth surfaces, making it harder for new plaque to accumulate.
This simple, pain-free procedure instantly reduces gum irritation, leaving your mouth feeling fresher and healthier.
Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
If gum disease has progressed beyond gingivitis, your dentist may recommend a deep cleaning. This two-step treatment involves:
Scaling
Removing plaque and tartar from deep under the gums.
Root Planing
Smoothing the root surfaces to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
This procedure helps stop gum bleeding, reduce inflammation, and prevent bacteria from re-entering gum pockets. It’s usually performed under local anesthesia for comfort and may take one or more sessions depending on the extent of the infection.
Antibacterial Rinses or Medications
To control infection and support healing, your dentist may prescribe antimicrobial mouthwash, antibiotic gels, or oral medications. These treatments target harmful bacteria that contribute to gum inflammation and bleeding. In some cases, antibiotics may be placed directly into the gum pockets for localized infection control.
Laser Gum Therapy
Modern dental clinic may use laser-assisted gum therapy as a minimally invasive alternative to traditional deep cleaning or surgery. Laser treatment effectively removes infected tissue, sterilizes gum pockets, and promotes faster healing with less discomfort and swelling.
Gum Surgery and Regenerative Procedures
In advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical treatment may be needed to restore gum and bone health.
Procedures include:
Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction) – The dentist gently lifts the gums to remove deep tartar buildup and smooth damaged bone before repositioning the tissue.
Gum Grafts – Used to replace receded gum tissue and cover exposed roots.
Bone Regeneration – Stimulates new bone growth to strengthen tooth support.
These treatments help prevent tooth loss, restore gum structure, and promote long-term oral stability.
Personalized Maintenance Plan
After your gums have healed, your dentist will create a custom maintenance schedule to monitor your progress and prevent recurrence. This may include more frequent cleanings (every 3–4 months), guidance on brushing and flossing techniques, and dietary or lifestyle recommendations to keep your gums strong.
How to Prevent Bleeding Gums
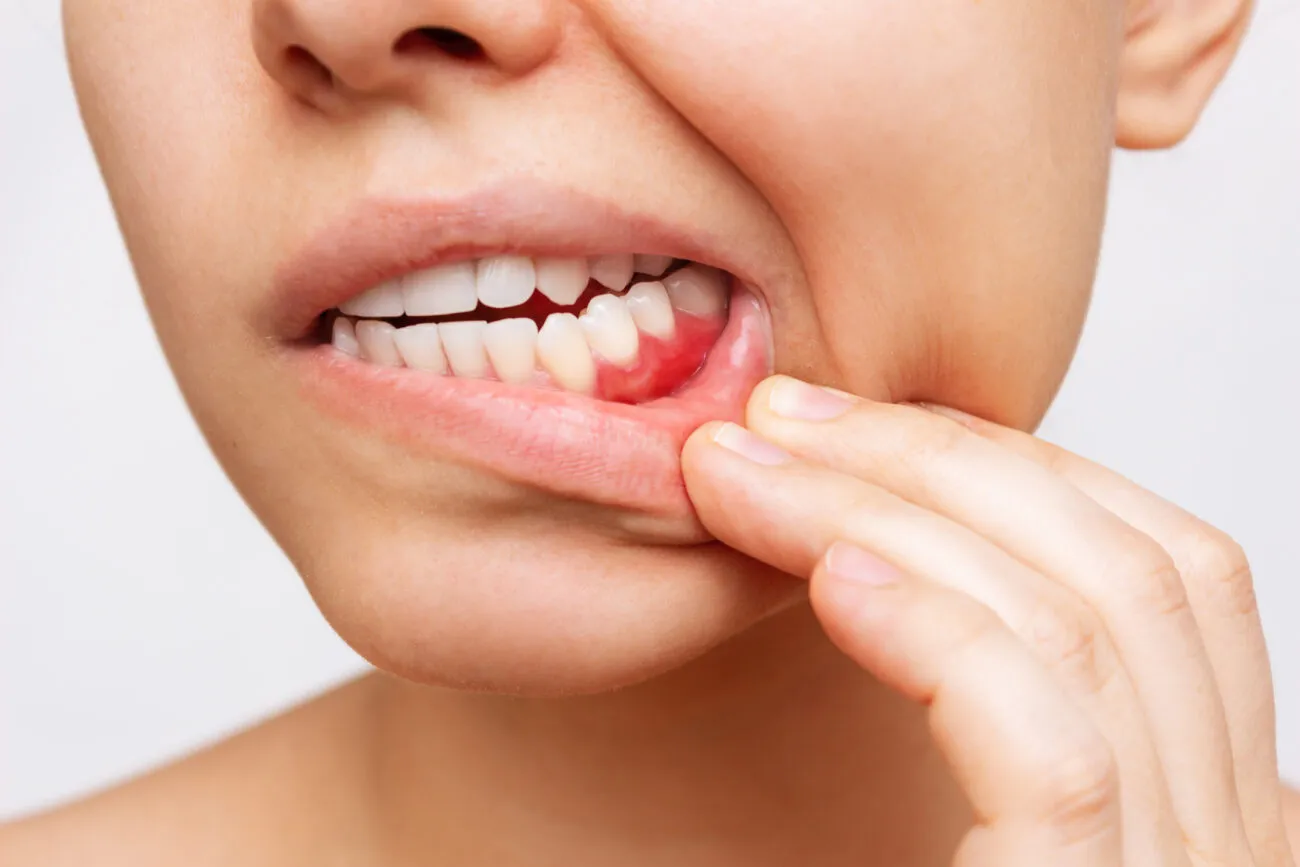
Healthy gums are easy to maintain but they need consistent attention and care. Preventing bleeding gums isn’t about drastic changes; it’s about building small, daily habits that protect your mouth from plaque, bacteria, and inflammation.
Here’s how you can keep your gums strong and healthy:
Brush Gently and Effectively
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to clean your teeth twice a day. Hard brushing can irritate or damage gum tissue, so focus on gentle circular motions rather than forceful scrubbing. Angle your brush at 45 degrees toward the gumline this helps remove plaque without causing trauma. Electric toothbrushes with pressure sensors can also be helpful if you tend to brush too hard.
Floss Every Day
Flossing is essential for removing food particles and plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach. If you’re new to flossing, it’s normal to see a little bleeding at first but don’t stop! Within a week or two of consistent flossing, your gums will strengthen and bleeding will usually disappear. For people with larger spaces between teeth, interdental brushes or water flossers can make cleaning easier and more effective.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
What you eat directly affects your gum health. Include foods rich in vitamin C (like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers) and vitamin K (such as spinach, broccoli, and kale). These nutrients help your gums heal, reduce inflammation, and strengthen blood vessels. Minimize sugary snacks and drinks, which feed bacteria that cause plaque buildup.
Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol
Smoking restricts blood flow to the gums and weakens your body’s ability to fight infection. Similarly, excessive alcohol use can irritate soft tissues and increase the risk of gum disease. If you smoke, consider quitting your gums will begin to recover and become healthier within weeks.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria while keeping your mouth moist. A dry mouth encourages bacterial growth and plaque accumulation, which can lead to gum irritation and bleeding.
Use Antibacterial Mouthwash
An alcohol-free antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque, kill bacteria, and keep your gums fresh and clean. Rinse once or twice daily especially after meals to enhance your oral hygiene routine.
Manage Stress and Medical Conditions
Stress can affect your immune system and make it harder for your gums to heal. Practice relaxation techniques, get enough sleep, and manage health conditions like diabetes, which can increase gum disease risk.
Regular Dental Checkups
Even with excellent home care, professional cleanings are vital. Dentists and hygienists can remove hardened tartar that brushing and flossing can’t eliminate. Schedule a check-up every six months, or more frequently if your dentist recommends it.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums might seem like a minor issue that happens when you brush too hard but in reality, it’s one of the first warning signs that your gums need attention. Ignoring it allows small problems like plaque buildup or gingivitis to develop into serious conditions such as periodontitis, which can lead to gum recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss. The best part? Bleeding gums are completely treatable especially when caught early. With a few simple changes to your daily routine and regular professional care, you can restore your gum health and protect your smile for years to come.
Start by using a soft-bristled toothbrush, brushing for two minutes twice daily, and flossing once a day with proper technique. Combine that with a healthy diet rich in vitamins C and K, regular hydration, and routine dental check-ups, and you’ll build a strong foundation for lifelong oral health.